How to Respond to a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR)

Table of Contents
All owners of online businesses, big or small, should be aware of how to manage Data Subject Access Requests (DSAR).
What is DSAR? It's a way for individuals — or data subjects — to ask your business to disclose which of their personal data you've collected and how you intend to use it. For many eCommerce businesses, the data subjects are their existing customers. But suppliers, contractors, business partners, and former employees are data subjects as well.
If your business hasn't received a DSAR yet, you likely will. That's why we suggest knowing how to respond to this type of information access request beforehand.
Here's a quick guide to responding to a Data Subject Access Request.
How Do You Respond to a GDPR DSAR?
Knowing the data subject access request process, as well as who's responsible for responding, will help you avoid penalties for missing due dates.
What's the Time Limit for Responding to a Subject Access Request?
How long to respond to a subject access request? Let's dive in and find out.
According to government regulations, a company should respond to a DSAR without delay, and supply the data within at least one month. Within this time, a reasonable search for the requested information should be undertaken. If multiple data requests are received or the request is complex, the time limit to deliver the data may be extended by two months.
Who's Responsible for Responding to a Subject Access Request?
Most businesses or companies have a Data Protection Officer — also referred to as the DPO — who has the duty of responding to DSARs. If your organization doesn't have a DPO, you should appoint one. Otherwise, an employee with data protection knowledge should complete the task.
There are multiple programs and courses available for employees to improve their data protection knowledge — a factor that all businesses can benefit from investing in.
How Do You Handle Data Requests?
So, your company has received a data request? Here's how to proceed:
1. Identify the Data Subject
When a data subject requests a subject access request, establish who they are and whether you have data for them on record. If you can't identify the person who made the request, you don't need to fulfill the request. However, you'll have to be able to prove that this was the case.
.png?width=483&height=471&name=Verify%20Identity%20(2).png)
2. Acknowledge That the Request Has Been Received
A request needs to be acknowledged as soon as possible. If information can be supplied, this needs to be done within a month (unless an extension is required). If more information is required from the person making the request, do it during this stage.
3. Establish Whether the Request Can Be Fulfilled
If a person can be identified, establish whether any restrictions or limitations apply to their request.
4. Consider Which Details To Include
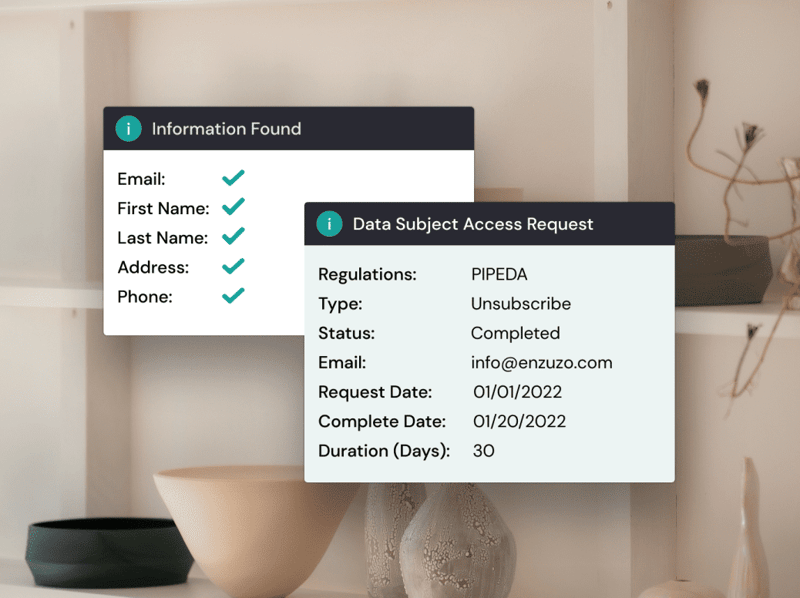
There are several types of data you may have to include in a data report, from the different categories of personal data you've stored to your reason for storing it. The data subject may mention the information they're looking for in their data request. Read on below for some more specific pieces of data you should be prepared to provide.
5. Fulfill the Request
Now it's time to fulfill the data subject's request. Once you've established which information you can and have to share, provide this data in an electronic form. Remember that failure to respond to a DSAR in a timely manner could lead to legal action and fines.
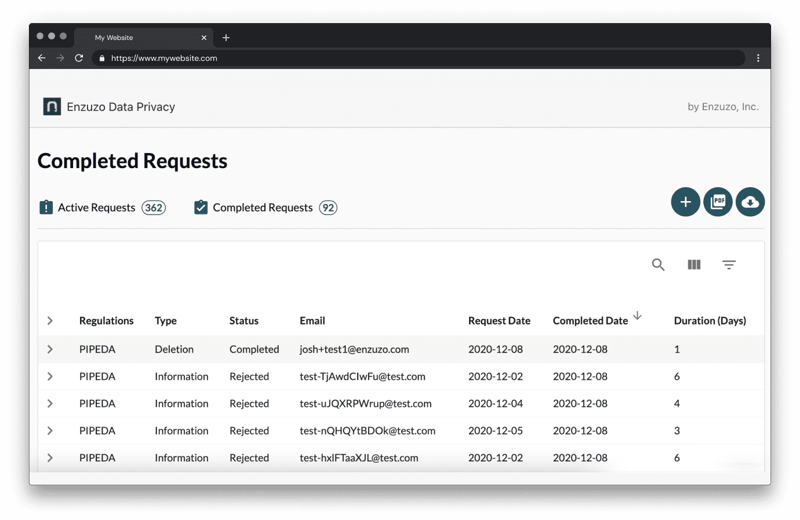
6. Record the Request Fulfillment
Keep track of data requests, namely what and who the request was for, when the data was requested, and when the request was fulfilled. This will save you from spending time on duplicate requests.
What Is Included in a Subject Access Request?
The actual data you need to include will change depending on the needs of the data subject. But the following pieces may be requested or included in your report:
- The purpose of the data collection
- How long the data will be stored
- The categories of collected personal data
- The source of the data, if the data subject did not provide it
- Who the data is being supplied or disclosed to, if applicable
- A request by the data subject to have their information removed from your company's database
How Far Back Can a DSAR Go?
You're required to provide subjects with data covering a one-year period. These data requests must be made in writing, and your company will have one month to provide the requested data.
Are Emails Included in a Subject Access Request?
If there aren't any laws preventing you from sharing third-party sensitive information, email communication may be included in a DSAR. A data subject will likely state the dates of the emails they're looking for, plus the names of the people they were communicating with.
Can a Company Refuse a Subject Access Request?
These six articles of the GDPR prevent your company from supplying or deleting certain data, even when it's requested in a DSAR:
- Protecting the Rights of Others (Articles 15 and 18)
Under these articles, data may not be provided to a subject if it would affect the rights and freedoms of others. This type of data may include trade secrets, copyright-protected software, or intellectual property.
- Keeping Data for Legal Reasons (Articles 16 and 17)
These articles require you to store data to comply with legal obligations, to perform a task for the public interest, or to exercise official authority. These requirements take priority over a data subject's request for their data to be deleted.
- When a Request is Unfounded (Article 20)
Under this article, if a request is unfounded or excessive and your company has a legitimate reason for collecting the information, the interests of the data subject take a back seat. Excessive and unfounded claims are described in more detail below.
- Using Data as a Defense (Article 21)
This article states that a company may store information for its defense in legal claims.
Can Information Be Redacted?
The personal information of third-party data subjects should be redacted if it doesn't apply to the person making the data request. This often happens when the requested data is found along with the personal data of other people.
As a rule of thumb, this includes any sensitive information that can be used to expose private information or commit fraud, which can include:
- social security numbers
- addresses
- driver's licenses
When Can You Refuse to Comply With a Request?
According to the UK Information Commissioner’s Office, a business can refuse to comply with a request if it's:
- Excessive: This may include overlapping requests, multiple requests in a short time, or a large-scale request that your company doesn't have the resources to respond to.
- Unfounded: This may occur when a request is malicious or the subject has implied that their request will be redacted in return for a free product or service.
Can Enzuzo Help Me Respond to a Data Subject Access Request?
Responding to DSARs can be daunting, which is where data management expert Enzuzo comes to the rescue. Enzuzo is an affordable and easy-to-manage way to automate data subject access requests for eCommerce.
Enzuzo helps businesses of all sizes minimize their risk of expensive privacy fines. How? By ensuring that you never miss a data request and can easily complete your DSAR responses on time.
In return, you gain your customers' trust by delivering or deleting their requested information and exercising transparency.
Don't go through your DSAR burdens alone. Start managing data requests today with the help of Enzuzo.

Paige Harris
Paige is the growth marketing lead at Enzuzo and host of The Living Lab podcast, providing insightful articles in the privacy space.